프로토타입에 대하여
위글을 다시 복습하면서 유추하면서 읽어야 하는 중요한 사실 정리:
1. 생성자 함수에서 프로토입에 접근할 때는 prototype를 쓰고 그 생성자가 만든 객체에서 프로토타입에 접근 할 때는 __proto__를 사용한다. 생성자 함수.__proto__는 Function.prototype 이다.
2.[[Prototype]]인터널 슬롯에 접근하기 위해서는 __proto__접근자를 사용한다(생성자 함수의 경우 __proto__사용시 Function.prototype에 접근함)
3. js엔진은 객체리터럴로 객체를 생성하지 않는다. 객체리터럴로 코딩해서 Object()생성자 함수로 객체를 생성한다(이와 다르게 생성자 함수를 정의하고 객체를 생성하면 당연히 그 생성자 함수로 부터 객체가 생성된다. 이것이 근본적으로 객체리터럴로부터 생성된 객체와 생성자 함수로부터 생성된 객체가 각각 다르게 다음과 같은프로토타입 체인을 갖게 되는 이유이다. (복습. 프로토타입 체인이란? 해당 객체에 접근하려는 메서드 혹은 프라퍼티가 없을 때 [[prototype]]이 가리키는 링크에 따라 자신의 부모 역할을 하는 프로토타입 객체의 프라퍼티 혹은 메서드를 차례로 검색하는 것)

===========================================================================================
- js엔진은 객체리터럴로 객체를 생성하지 않는다. 객체리터럴로 코딩해도 Object()생성자 함수로 객체를 생성한다.
==>> 객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성된 객체는 결국 내장 함수(Built-in)인 Object() 생성자 함수로 객체를 생성하는 것을 단순화시킨 것이다. 자바스크립트 엔진은 객체 리터럴로 객체를 생성하는 코드를 만나면 내부적으로 Object() 생성자 함수를 사용하여 객체를 생성한다.
-[[Protoyupe]]은 __proto__로 생각하면 된다.
-(내생각)생성자함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입체인 그림에서 생성자함수객체는 내가 함수를 정의하면 생기고, 생성자함수로 생성된 인스턴스 객체는 내가 new연산자를 생성자 함수와 함께 사용하면 생기는 객체로써 2개 모두 내가 코딩해준 것에서 생기는 객체들이다. 하지만 생성자이름.prototype 객체는 생성자함수를 정의해주면 자동으로 생기는 객체같다.
-Object 생성자 함수이건 그냥 생성자 함수이건 생성자 함수라면 무조건 prototype 프라퍼티를 가지고 있다.그리고 오직 생성자 함수만이 prototype 프라퍼티를 갖느다. 하지만 생성자 함수라고 하여 __proto__를 사용하지 않는것은 아니다. 아래그림의 동그라미3번이 그러하다.
var person = {
name: 'Lee',
gender: 'male',
sayHello: function(){
console.log('Hi! my name is ' + this.name);
}
};
console.dir(person);
console.log(person.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ① true
console.log(Object.prototype.constructor === Object); // ② true
console.log(Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype); // ③ true
console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ④ true
- 프로토타입은 클래스, 객체의 내용복사 없이도 상속을 구현할 수 있게 해준다. 프로토타입은 연결이다.
-객체는 자신의 원형이라고 할수 있는 객체가 있다면 그 객체를 가리키는 __proto__링크를 자동으로 가짐.
(즉, newObj는 old의 자식 객체가 됨)
1. 프로토타입 객체
Java, C++과 같은 클래스 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어와 달리 자바스크립트는 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어이다. 따라서 자바스크립트의 동작 원리를 이해하기 위해서는 프로토타입의 개념을 잘 이해하고 있어야 한다.
클래스 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어는 객체 생성 이전에 클래스를 정의하고 이를 통해 객체(인스턴스)를 생성한다. 하지만 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어는 클래스 없이(Class-less)도 (ECMAScript 6에서 클래스가 추가되었다) 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
자바스크립트의 모든 객체는 자신의 부모 역할을 담당하는 객체와 연결되어 있다. 그리고 이것은 마치 객체 지향의 상속 개념과 같이 부모 객체의 프로퍼티 또는 메소드를 상속받아 사용할 수 있게 한다. 이러한 부모 객체를 Prototype(프로토타입) 객체 또는 줄여서 Prototype(프로토타입)이라 한다.
Prototype 객체는 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 각각의 객체에 공유 프로퍼티를 제공하기 위해 사용한다.
var student = {
name: 'Lee',
score: 90
};
// student에는 hasOwnProperty 메소드가 없지만 아래 구문은 동작한다.
console.log(student.hasOwnProperty('name')); // true
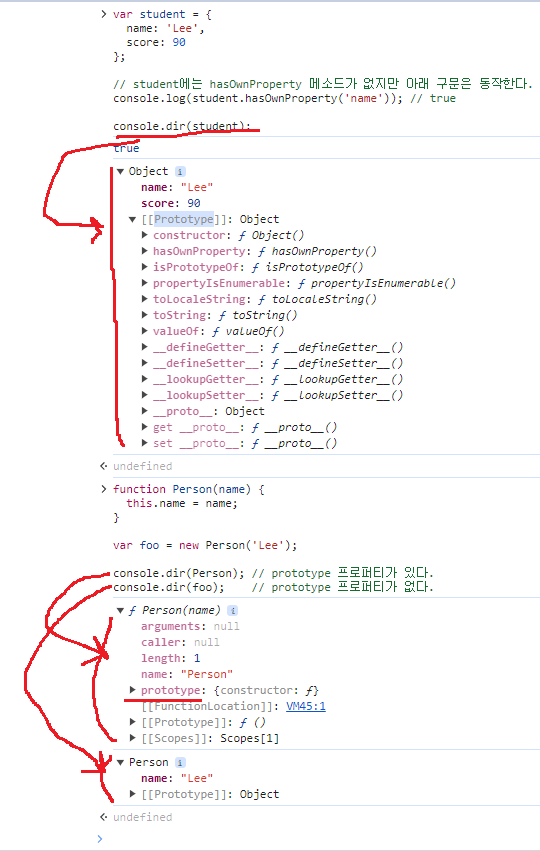
console.dir(student);

Google chrome에서 student 객체 출력 결과
ECMAScript spec에서는 자바스크립트의 모든 객체는 [[Prototype]]이라는 인터널 슬롯(internal slot)를 가진다. [[Prototype]]의 값은 null 또는 객체이며 상속을 구현하는데 사용된다. [[Prototype]] 객체의 데이터 프로퍼티는 get 액세스를 위해 상속되어 자식 객체의 프로퍼티처럼 사용할 수 있다. 하지만 set 액세스는 허용되지 않는다. 라고 되어있다.
[[Prototype]]의 값은 Prototype(프로토타입) 객체이며 __proto__ accessor property로 접근할 수 있다. __proto__ 프로퍼티에 접근하면 내부적으로 Object.getPrototypeOf가 호출되어 프로토타입 객체를 반환한다.
student 객체는 __proto__ 프로퍼티로 자신의 부모 객체(프로토타입 객체)인 Object.prototype을 가리키고 있다.
var student = {
name: 'Lee',
score: 90
}
console.log(student.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
객체를 생성할 때 프로토타입은 결정된다. 결정된 프로토타입 객체는 다른 임의의 객체로 변경할 수 있다. 이것은 부모 객체인 프로토타입을 동적으로 변경할 수 있다는 것을 의미한다. 이러한 특징을 활용하여 객체의 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
#2. [[Prototype]] vs prototype 프로퍼티
모든 객체는 자신의 프로토타입 객체를 가리키는 [[Prototype]] 인터널 슬롯(internal slot) 을 갖으며 상속을 위해 사용된다.
함수도 객체이므로 [[Prototype]] 인터널 슬롯을 갖는다. 그런데 함수 객체는 일반 객체와는 달리 prototype 프로퍼티도 소유하게 된다.
주의해야 할 것은 prototype 프로퍼티는 프로토타입 객체를 가리키는 [[Prototype]] 인터널 슬롯은 다르다는 것이다. prototype 프로퍼티와 [[Prototype]]은 모두 프로토타입 객체를 가리키지만 관점의 차이가 있다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var foo = new Person('Lee');
console.dir(Person); // prototype 프로퍼티가 있다.
console.dir(foo); // prototype 프로퍼티가 없다.
- [[Prototype]]
- 함수를 포함한 모든 객체가 가지고 있는 인터널 슬롯이다.
- 객체의 입장에서 자신의 부모 역할을 하는 프로토타입 객체를 가리키며 함수 객체의 경우 Function.prototype를 가리킨다. 그 이유에 대해서는 4.2 생성자 함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입 체인을 참조하기 바란다.
- console.log(Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype);
- prototype 프로퍼티
- 함수 객체만 가지고 있는 프로퍼티이다.
- 함수 객체가 생성자로 사용될 때 이 함수를 통해 생성될 객체의 부모 역할을 하는 객체(프로토타입 객체)를 가리킨다.
- console.log(Person.prototype === foo.__proto__);
#3. constructor 프로퍼티
프로토타입 객체는 constructor 프로퍼티를 갖는다. 이 constructor 프로퍼티는 객체의 입장에서 자신을 생성한 객체를 가리킨다.
예를 들어 Person() 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체를 foo라 하자. 이 foo 객체를 생성한 객체는 Person() 생성자 함수이다. 이때 foo 객체 입장에서 자신을 생성한 객체는 Person() 생성자 함수이며, foo 객체의 프로토타입 객체는 Person.prototype이다. 따라서 프로토타입 객체 Person.prototype의 constructor 프로퍼티는 Person() 생성자 함수를 가리킨다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var foo = new Person('Lee');
// Person() 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체를 생성한 객체는 Person() 생성자 함수이다.
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person);
// foo 객체를 생성한 객체는 Person() 생성자 함수이다.
console.log(foo.constructor === Person);
// Person() 생성자 함수를 생성한 객체는 Function() 생성자 함수이다.
console.log(Person.constructor === Function);
#4. Prototype chain
자바스크립트는 특정 객체의 프로퍼티나 메소드에 접근하려고 할 때 해당 객체에 접근하려는 프로퍼티 또는 메소드가 없다면 [[Prototype]]이 가리키는 링크를 따라 자신의 부모 역할을 하는 프로토타입 객체의 프로퍼티나 메소드를 차례대로 검색한다. 이것을 프로토타입 체인이라 한다.
var student = {
name: 'Lee',
score: 90
}
// Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty()
console.log(student.hasOwnProperty('name')); // true
student 객체는 hasOwnProperty 메소드를 가지고 있지 않으므로 에러가 발생하여야 하나 정상적으로 결과가 출력되었다. 이는 student 객체의 [[Prototype]]이 가리키는 링크를 따라가서 student 객체의 부모 역할을 하는 프로토타입 객체(Object.prototype)의 메소드 hasOwnProperty를 호출하였기 때문에 가능한 것이다.
var student = {
name: 'Lee',
score: 90
}
console.dir(student);
console.log(student.hasOwnProperty('name')); // true
console.log(student.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty')); // true
#4.1 객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입 체인
객체 생성 방법은 3가지가 있다.
- 객체 리터럴
- 생성자 함수
- Object() 생성자 함수
객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성된 객체는 결국 내장 함수(Built-in)인 Object() 생성자 함수로 객체를 생성하는 것을 단순화시킨 것이다. 자바스크립트 엔진은 객체 리터럴로 객체를 생성하는 코드를 만나면 내부적으로 Object() 생성자 함수를 사용하여 객체를 생성한다.
Object() 생성자 함수는 물론 함수이다. 따라서 함수 객체인 Object() 생성자 함수는 일반 객체와 달리 prototype 프로퍼티가 있다.
- prototype 프로퍼티는 함수 객체가 생성자로 사용될 때 이 함수를 통해 생성된 객체의 부모 역할을 하는 객체, 즉 프로토타입 객체를 가리킨다.
- [[Prototype]]은 객체의 입장에서 자신의 부모 역할을 하는 객체, 즉 프로토타입 객체를 가리킨다.
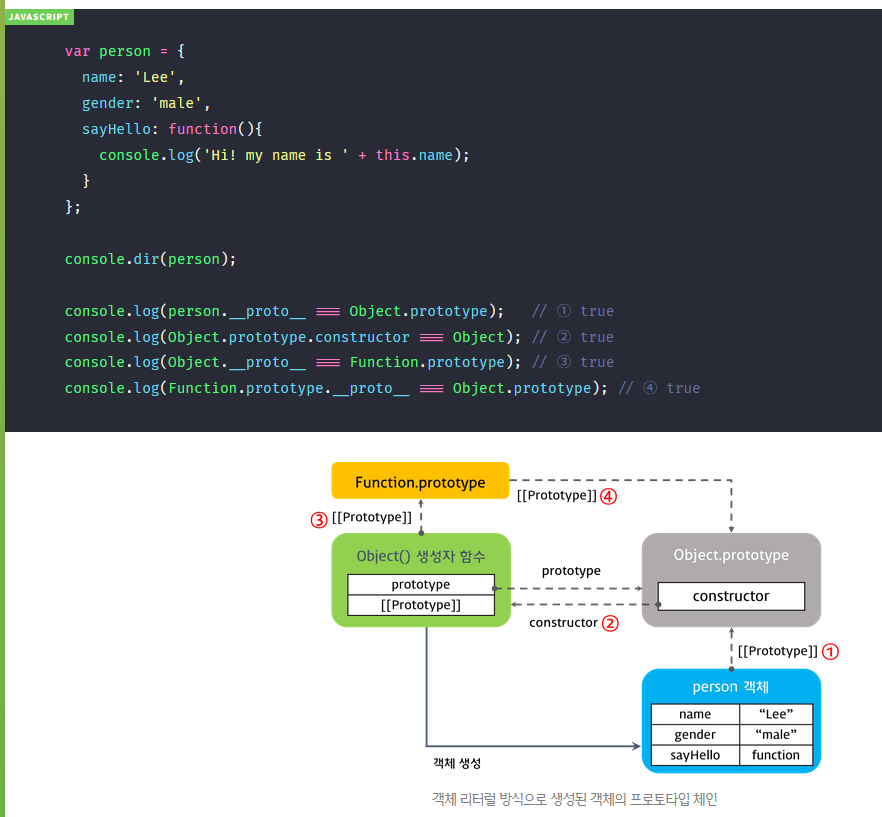
var person = {
name: 'Lee',
gender: 'male',
sayHello: function(){
console.log('Hi! my name is ' + this.name);
}
};
console.dir(person);
console.log(person.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ① true
console.log(Object.prototype.constructor === Object); // ② true
console.log(Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype); // ③ true
console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ④ true
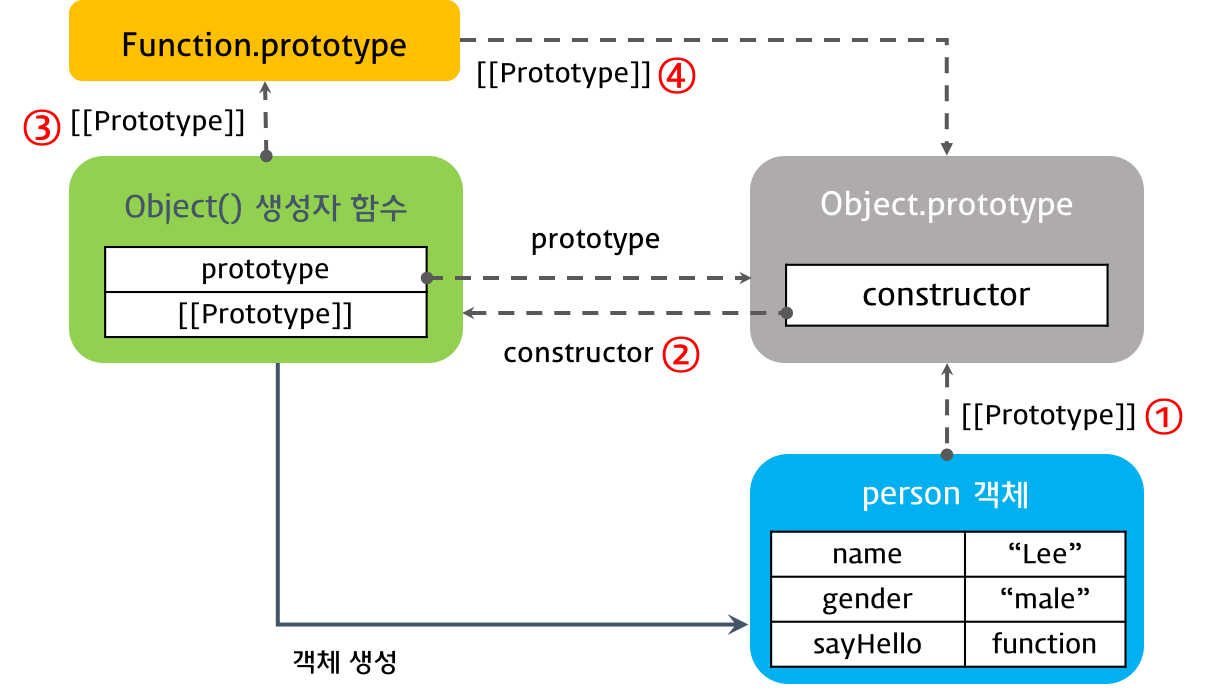
객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입 체인
결론적으로 객체 리터럴을 사용하여 객체를 생성한 경우, 그 객체의 프로토타입 객체는 Object.prototype이다.
#4.2 생성자 함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입 체인
생성자 함수로 객체를 생성하기 위해서는 우선 생성자 함수를 정의하여야 한다.
함수를 정의하는 방식은 3가지가 있다.
- 함수선언식(Function declaration)
- 함수표현식(Function expression)
- Function() 생성자 함수
함수표현식으로 함수를 정의할 때 함수 리터럴 방식을 사용한다.
var square = function(number) {
return number * number;
};
함수선언식의 경우 자바스크립트 엔진이 내부적으로 기명 함수표현식으로 변환한다.
var square = function square(number) {
return number * number;
};
결국 함수선언식, 함수표현식 모두 함수 리터럴 방식을 사용한다. 함수 리터럴 방식은 Function() 생성자 함수로 함수를 생성하는 것을 단순화 시킨 것이다.
즉, 3가지 함수 정의 방식은 결국 Function() 생성자 함수를 통해 함수 객체를 생성한다, 따라서 어떠한 방식으로 함수 객체를 생성하여도 모든 함수 객체의 prototype 객체는 Function.prototype이다. 생성자 함수도 함수 객체이므로 생성자 함수의 prototype 객체는 Function.prototype이다.
이제 객체의 관점에서 prototype 객체를 살펴보자.
객체를 생성하는 방식은 3가지가 있다. 3가지 객체 생성 방식에 의해 생성된 객체의 prototype 객체를 정리해 보면 아래와 같다.
| 객체 리터럴 | Object() 생성자 함수 | Object.prototype |
| Object() 생성자 함수 | Object() 생성자 함수 | Object.prototype |
| 생성자 함수 | 생성자 함수 | 생성자 함수 이름.prototype |
객체 생성 방식 엔진의 객체 생성 인스턴스의 prototype 객체
function Person(name, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.sayHello = function(){
console.log('Hi! my name is ' + this.name);
};
}
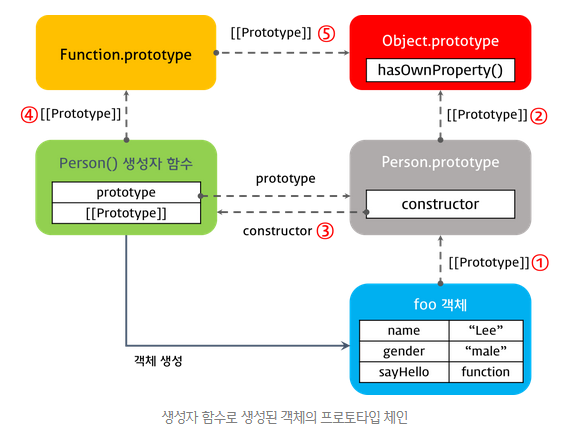
var foo = new Person('Lee', 'male');
console.dir(Person);
console.dir(foo);
console.log(foo.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // ① true
console.log(Person.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ② true
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); // ③ true
console.log(Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype); // ④ true
console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ⑤ true
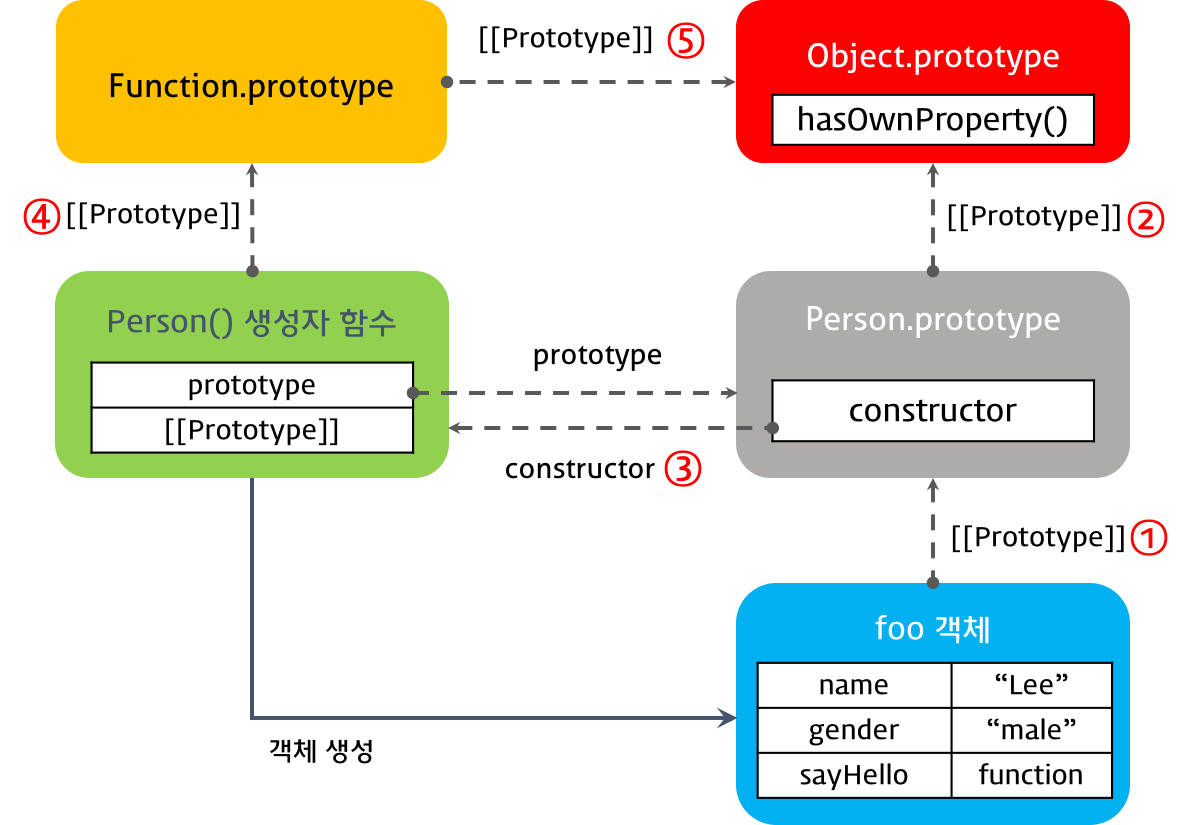
생성자 함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입 체인
foo 객체의 프로토타입 객체 Person.prototype 객체와 Person() 생성자 함수의 프로토타입 객체인 Function.prototype의 프로토타입 객체는 Object.prototype 객체이다.
이는 객체 리터럴 방식이나 생성자 함수 방식이나 결국은 모든 객체의 부모 객체인 Object.prototype 객체에서 프로토타입 체인이 끝나기 때문이다. 이때 Object.prototype 객체를 프로토타입 체인의 종점(End of prototype chain)이라 한다.
#5. 프로토타입 객체의 확장
프로토타입 객체도 객체이므로 일반 객체와 같이 프로퍼티를 추가/삭제할 수 있다. 그리고 이렇게 추가/삭제된 프로퍼티는 즉시 프로토타입 체인에 반영된다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var foo = new Person('Lee');
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log('Hi! my name is ' + this.name);
};
foo.sayHello();
생성자 함수 Person은 프로토타입 객체 Person.prototype와 prototype 프로퍼티에 의해 바인딩되어 있다. Person.prototype 객체는 일반 객체와 같이 프로퍼티를 추가/삭제가 가능하다. 위의 예에서는 Person.prototype 객체에 메소드 sayHello를 추가하였다. 이때 sayHello 메소드는 프로토타입 체인에 반영된다. 따라서 생성자 함수 Person에 의해 생성된 모든 객체는 프로토타입 체인에 의해 부모객체인 Person.prototype의 메소드를 사용할 수 있게 되었다.
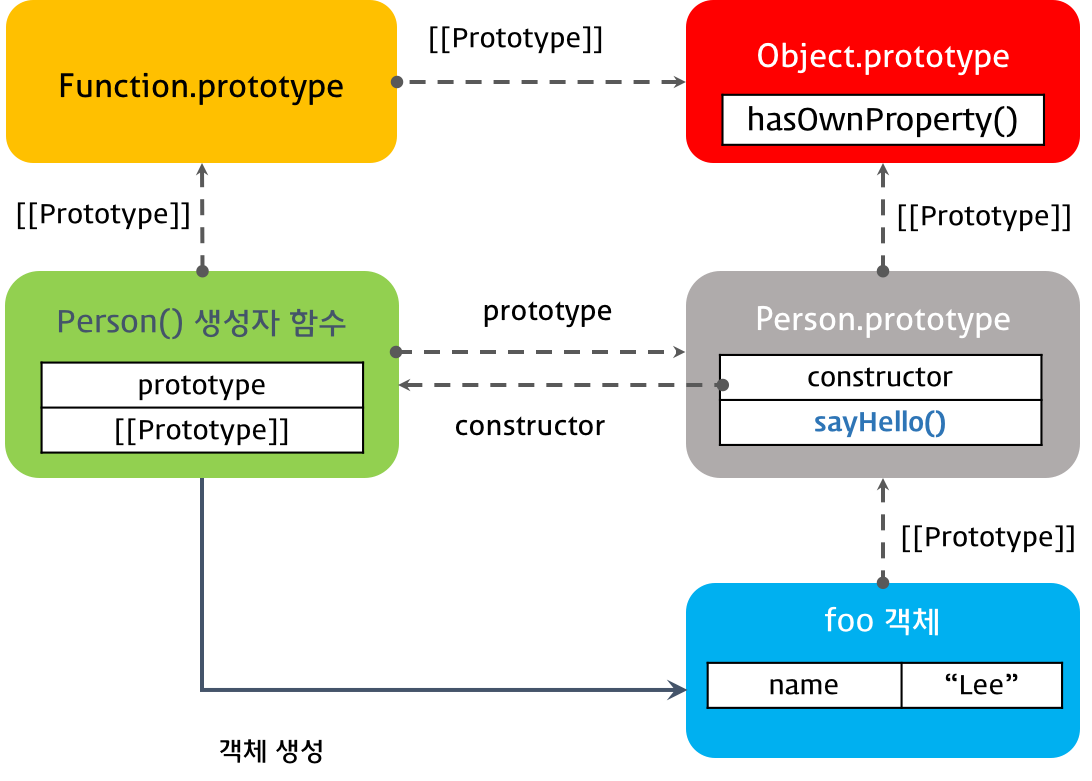
#6. 원시 타입(Primitive data type)의 확장
자바스크립트에서 원시 타입(숫자, 문자열, boolean, null, undefined)을 제외한 모든것은 객체이다. 그런데 아래 예제를 살펴보면 원시 타입인 문자열이 객체와 유사하게 동작한다.
var str = 'test';
console.log(typeof str); // string
console.log(str.constructor === String); // true
console.dir(str); // test
var strObj = new String('test');
console.log(typeof strObj); // object
console.log(strObj.constructor === String); // true
console.dir(strObj);
// {0: "t", 1: "e", 2: "s", 3: "t", length: 4, __proto__: String, [[PrimitiveValue]]: "test" }
console.log(str.toUpperCase()); // TEST
console.log(strObj.toUpperCase()); // TEST
원시 타입 문자열과 String() 생성자 함수로 생성한 문자열 객체의 타입은 분명이 다르다. 원시 타입은 객체가 아니므로 프로퍼티나 메소드를 가질수 없다. 하지만 원시 타입으로 프로퍼티나 메소드를 호출할 때 원시 타입과 연관된 객체로 일시적으로 변환되어 프로토타입 객체를 공유하게 된다.
원시 타입은 객체가 아니므로 프로퍼티나 메소드를 직접 추가할 수 없다.
var str = 'test';
// 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
str.myMethod = function () {
console.log('str.myMethod');
};
str.myMethod(); // Uncaught TypeError: str.myMethod is not a function
하지만 String 객체의 프로토타입 객체 String.prototype에 메소드를 추가하면 원시 타입, 객체 모두 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
var str = 'test';
String.prototype.myMethod = function () {
return 'myMethod';
};
console.log(str.myMethod()); // myMethod
console.log('string'.myMethod()); // myMethod
console.dir(String.prototype);
앞서 살펴본 바와 같이 모든 객체는 프로토타입 체인에 의해 Object.prototype 객체의 메소드를 사용할 수 있었다. Object.prototype 객체는 프로토타입 체인의 종점으로 모든 객체가 사용할 수 있는 메소드를 갖는다.
이후 살펴보게 될 Built-in object(내장 객체)의 Global objects (Standard Built-in Objects)인 String, Number, Array 객체 등이 가지고 있는 표준 메소드는 프로토타입 객체인 String.prototype, Number.prototype, Array.prototype 등에 정의되어 있다. 이들 프로토타입 객체 또한 Object.prototype를 프로토타입 체인에 의해 자신의 프로토타입 객체로 연결한다.
자바스크립트는 표준 내장 객체의 프로토타입 객체에 개발자가 정의한 메소드의 추가를 허용한다.
var str = 'test';
String.prototype.myMethod = function() {
return 'myMethod';
}
console.log(str.myMethod());
console.dir(String.prototype);
console.log(str.__proto__ === String.prototype); // ① true
console.log(String.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ② true
console.log(String.prototype.constructor === String); // ③ true
console.log(String.__proto__ === Function.prototype); // ④ true
console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // ⑤ true
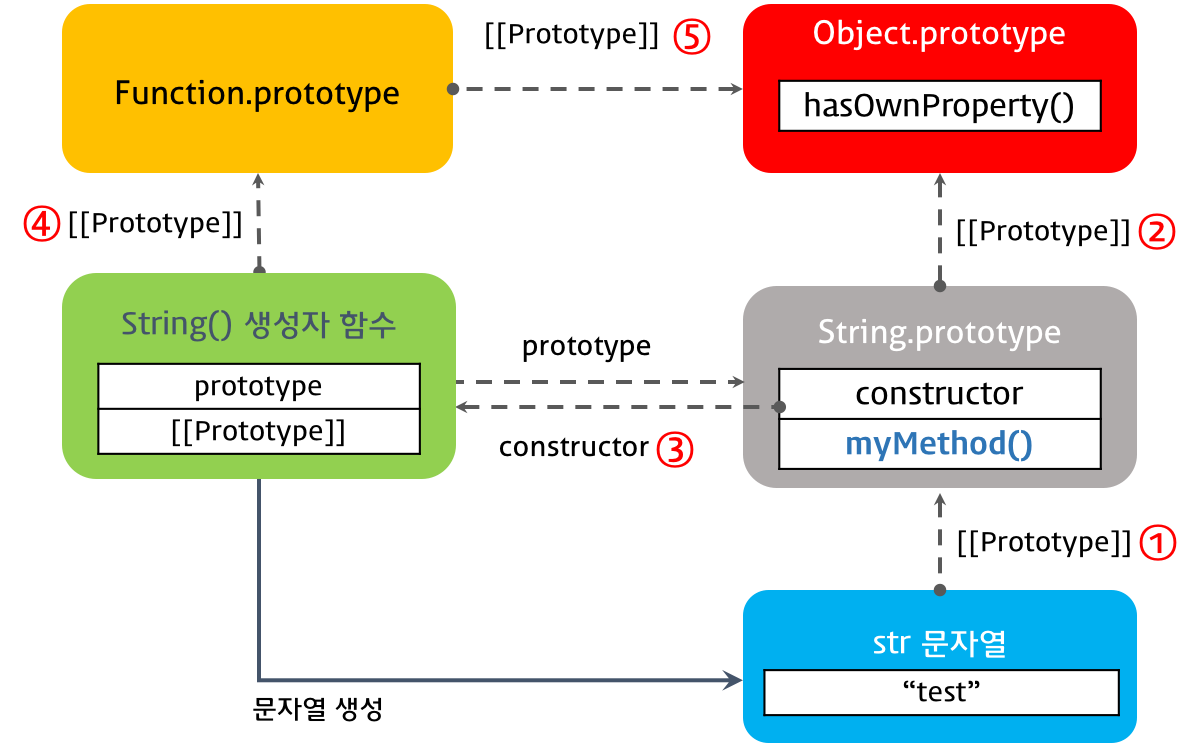
#7. 프로토타입 객체의 변경
객체를 생성할 때 프로토타입은 결정된다. 결정된 프로토타입 객체는 다른 임의의 객체로 변경할 수 있다. 이것은 부모 객체인 프로토타입을 동적으로 변경할 수 있다는 것을 의미한다. 이러한 특징을 활용하여 객체의 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
이때 주의할 것은 프로토타입 객체를 변경하면
- 프로토타입 객체 변경 시점 이전에 생성된 객체 기존 프로토타입 객체를 [[Prototype]]에 바인딩한다.
- 프로토타입 객체 변경 시점 이후에 생성된 객체 변경된 프로토타입 객체를 [[Prototype]]에 바인딩한다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var foo = new Person('Lee');
// 프로토타입 객체의 변경
Person.prototype = { gender: 'male' };
var bar = new Person('Kim');
console.log(foo.gender); // undefined
console.log(bar.gender); // 'male'
console.log(foo.constructor); // ① Person(name)
console.log(bar.constructor); // ② Object()
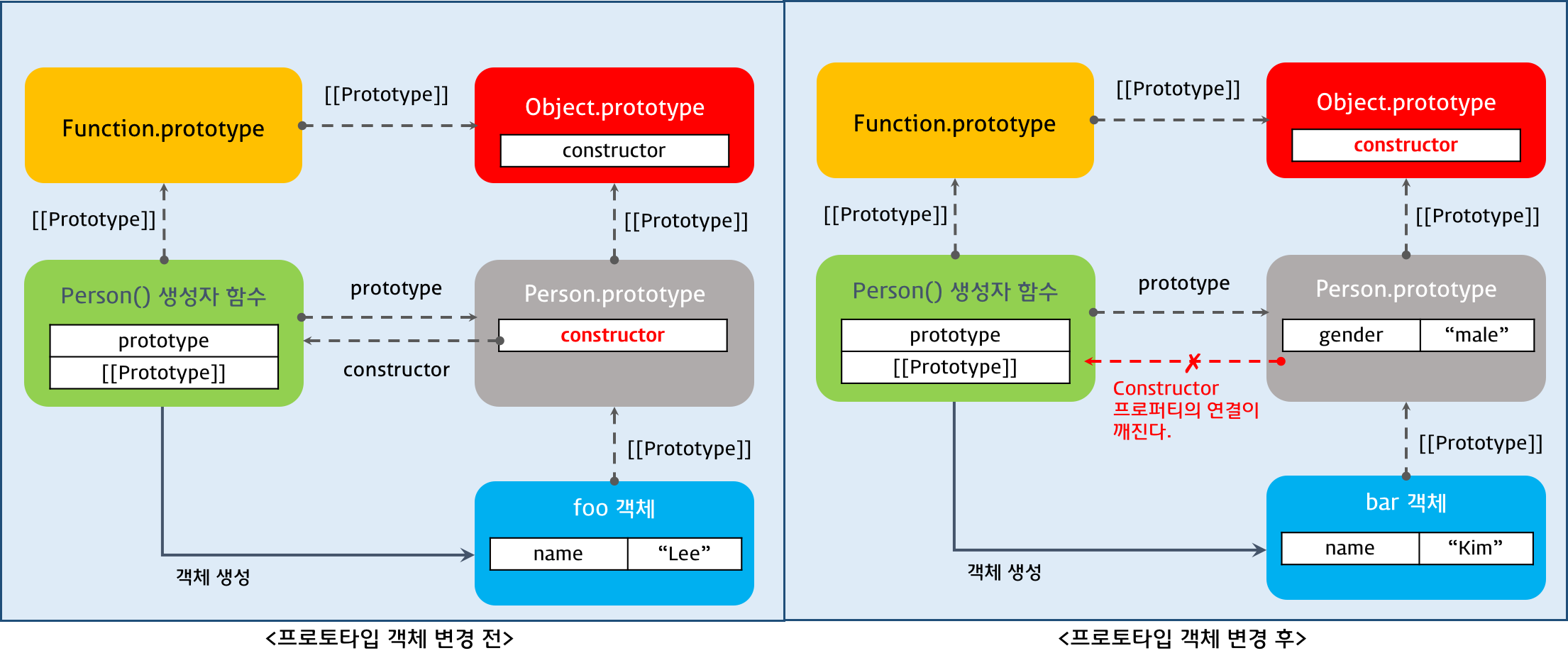
① constructor 프로퍼티는 Person() 생성자 함수를 가리킨다.
② 프로토타입 객체 변경 후, Person() 생성자 함수의 Prototype 프로퍼티가 가리키는 프로토타입 객체를 일반 객체로 변경하면서 Person.prototype.constructor 프로퍼티도 삭제되었다. 따라서 프로토타입 체인에 의해 bar.constructor의 값은 프로토타입 체이닝에 의해 Object.prototype.constructor 즉 Object() 생성자 함수가 된다.
#8. 프로토타입 체인 동작 조건
객체의 프로퍼티를 참조하는 경우, 해당 객체에 프로퍼티가 없는 경우, 프로토타입 체인이 동작한다.
객체의 프로퍼티에 값을 할당하는 경우, 프로토타입 체인이 동작하지 않는다. 이는 객체에 해당 프로퍼티가 있는 경우, 값을 재할당하고 해당 프로퍼티가 없는 경우는 해당 객체에 프로퍼티를 동적으로 추가하기 때문이다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.gender = 'male'; // ①
var foo = new Person('Lee');
var bar = new Person('Kim');
console.log(foo.gender); // ① 'male'
console.log(bar.gender); // ① 'male'
// 1. foo 객체에 gender 프로퍼티가 없으면 프로퍼티 동적 추가
// 2. foo 객체에 gender 프로퍼티가 있으면 해당 프로퍼티에 값 할당
foo.gender = 'female'; // ②
console.log(foo.gender); // ② 'female'
console.log(bar.gender); // ① 'male'
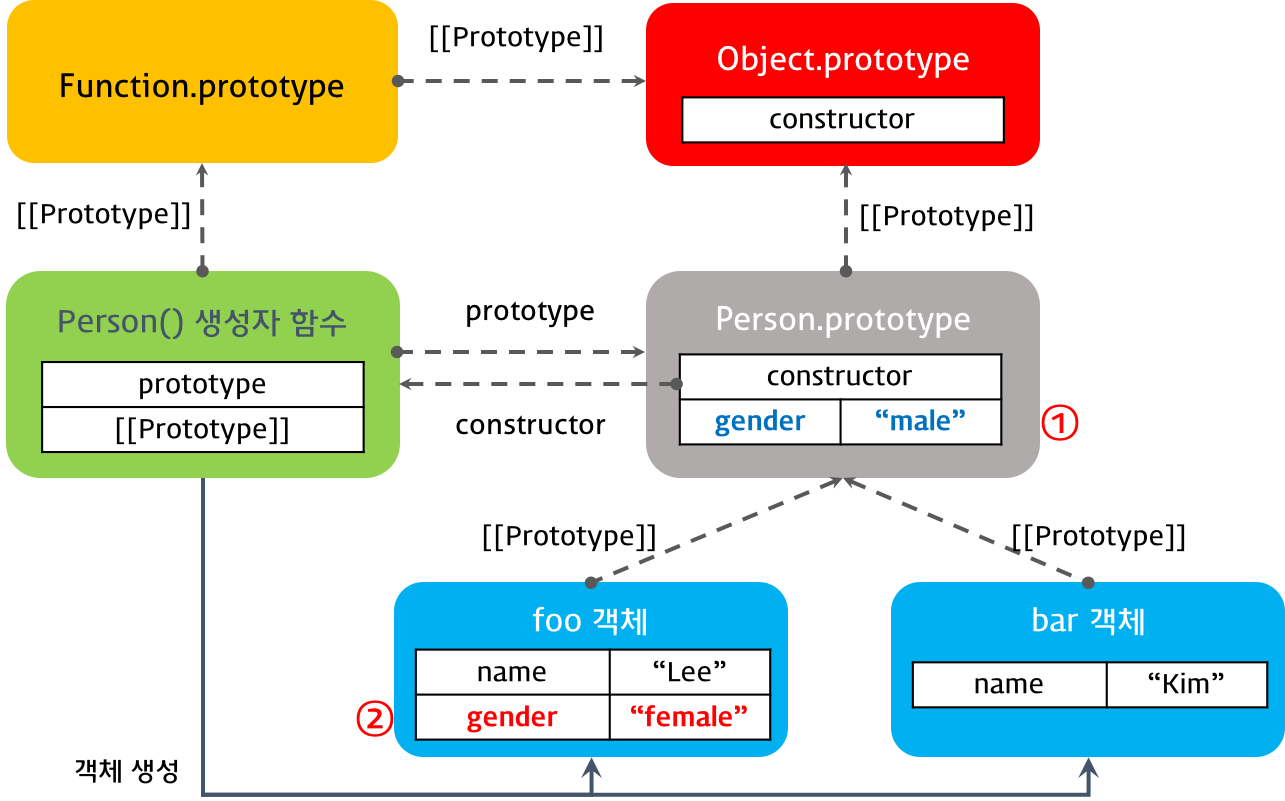
foo 객체의 gender 프로퍼티에 값을 할당하면 프로토타입 체인이 발생하여 Person.prototype 객체의 gender 프로퍼티에 값을 할당하는 것이 아니라 foo 객체에 프로퍼티를 동적으로 추가한다.